Is a Down Syndrome Baby More Likely to Be Breech
Down syndrome is a status in which a person has an actress chromosome.
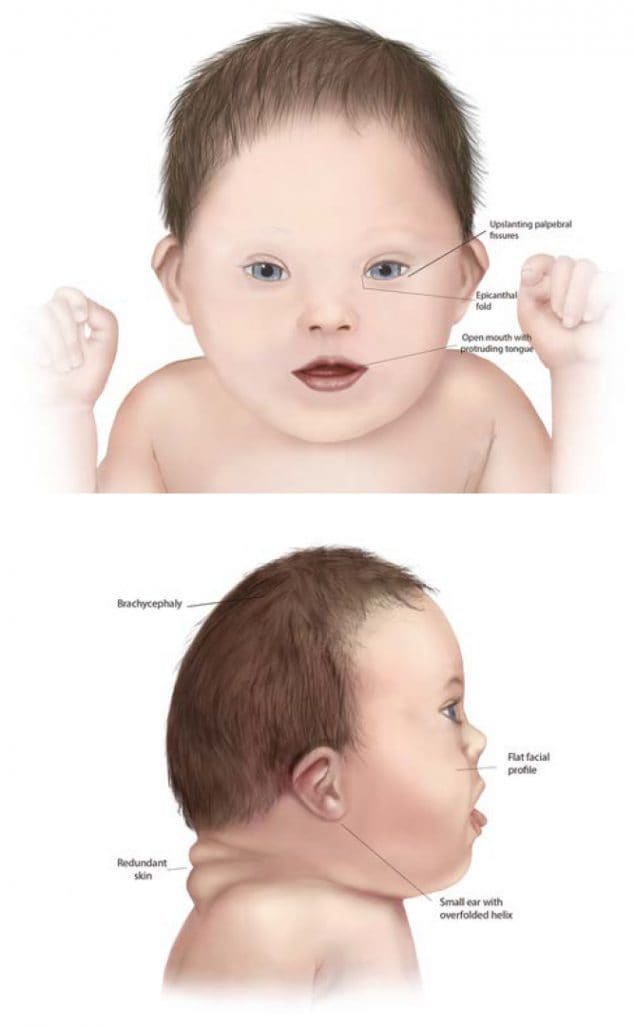
What is Down's syndrome?
Down syndrome is a status in which a person has an actress chromosome. Chromosomes are modest "packages" of genes in the body. They make up one's mind how a infant's torso forms and functions equally it grows during pregnancy and after birth. Typically, a infant is built-in with 46 chromosomes. Babies with Down's syndrome take an extra copy of one of these chromosomes, chromosome 21. A medical term for having an extra copy of a chromosome is 'trisomy.' Down syndrome is also referred to as Trisomy 21. This extra re-create changes how the babe's body and brain develop, which can crusade both mental and physical challenges for the baby.
Even though people with Downward syndrome might act and look similar, each person has different abilities. People with Down syndrome normally accept an IQ (a measure out of intelligence) in the mildly-to-moderately depression range and are slower to speak than other children.
Some common concrete features of Downward syndrome include:
- A flattened face, especially the span of the nose
- Almond-shaped eyes that slant up
- A curt neck
- Pocket-size ears
- A tongue that tends to stick out of the oral fissure
- Tiny white spots on the iris (colored part) of the eye
- Small easily and feet
- A single line across the palm of the hand (palmar crease)
- Pocket-sized pinky fingers that sometimes curve toward the pollex
- Poor muscle tone or loose joints
- Shorter in acme as children and adults
How Many Babies are Built-in with Down Syndrome?
Down syndrome remains the near common chromosomal condition diagnosed in the United states. Each year, about half dozen,000 babies born in the United States take Down syndrome. This means that Down's syndrome occurs in about 1 in every 700 babies.one
Types of Down syndrome
At that place are 3 types of Down syndrome. People often can't tell the divergence between each blazon without looking at the chromosomes because the concrete features and behaviors are like.
- Trisomy 21: About 95% of people with Down's syndrome have Trisomy 21.2 With this type of Down syndrome, each cell in the body has three separate copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual 2 copies.
- Translocation Down syndrome: This type accounts for a small percentage of people with Downward syndrome (about 3%).ii This occurs when an extra part or a whole extra chromosome 21 is nowadays, only it is attached or "trans-located" to a different chromosome rather than being a split up chromosome 21.
- Mosaic Downward syndrome: This type affects almost ii% of the people with Down syndrome.2 Mosaic means mixture or combination. For children with mosaic Down syndrome, some of their cells have 3 copies of chromosome 21, but other cells take the typical two copies of chromosome 21. Children with mosaic Down syndrome may have the same features equally other children with Down syndrome. Even so, they may take fewer features of the condition due to the presence of some (or many) cells with a typical number of chromosomes.
Causes and Risk Factors
- The extra chromosome 21 leads to the concrete features and developmental challenges that can occur among people with Down's syndrome. Researchers know that Downwards syndrome is caused by an extra chromosome, merely no one knows for sure why Downwards syndrome occurs or how many different factors play a function.
- I factor that increases the gamble for having a baby with Down's syndrome is the mother's age. Women who are 35 years or older when they become meaning are more likely to have a pregnancy affected by Down's syndrome than women who become pregnant at a younger age.3-fiveAll the same, the bulk of babies with Down syndrome are born to mothers less than 35 years old, because at that place are many more births amid younger women.half dozen,7
Diagnosis
At that place are two bones types of tests available to observe Down's syndrome during pregnancy: screening tests and diagnostic tests. A screening examination can tell a woman and her healthcare provider whether her pregnancy has a lower or higher chance of having Down syndrome. Screening tests do non provide an absolute diagnosis, simply they are safer for the mother and the developing babe. Diagnostic tests can typically detect whether or not a baby will accept Down syndrome, only they tin be more risky for the mother and developing baby. Neither screening nor diagnostic tests can predict the full impact of Down's syndrome on a baby; no i can predict this.
Screening Tests
Screening tests often include a combination of a blood test, which measures the amount of various substances in the mother's blood (e.grand., MS-AFP, Triple Screen, Quad-screen), and an ultrasound, which creates a movie of the baby. During an ultrasound, one of the things the technician looks at is the fluid behind the baby's cervix. Actress fluid in this region could indicate a genetic problem. These screening tests tin can help determine the baby'south chance of Down's syndrome. Rarely, screening tests can give an abnormal result even when at that place is nothing wrong with the infant. Sometimes, the test results are normal and yet they miss a problem that does exist.
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic tests are commonly performed after a positive screening examination in social club to confirm a Downwards syndrome diagnosis. Types of diagnostic tests include:
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)—examines textile from the placenta
- Amniocentesis—examines the amniotic fluid (the fluid from the sac surrounding the baby)
- Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS)—examines blood from the umbilical string
These tests look for changes in the chromosomes that would indicate a Down syndrome diagnosis.
Other Wellness Problems
Many people with Down syndrome have the common facial features and no other major birth defects. However, some people with Down syndrome might accept one or more major birth defects or other medical bug. Some of the more common health problems among children with Downwards syndrome are listed beneath.eight
- Hearing loss
- Obstructive sleep apnea, which is a status where the person's animate temporarily stops while asleep
- Ear infections
- Centre diseases
- Eye defects present at birth
Health care providers routinely monitor children with Downwardly syndrome for these conditions.
Treatments
Down's syndrome is a lifelong condition. Services early on in life volition often help babies and children with Down's syndrome to ameliorate their physical and intellectual abilities. Nigh of these services focus on helping children with Down's syndrome develop to their full potential. These services include speech, occupational, and concrete therapy, and they are typically offered through early intervention programs in each land. Children with Downward syndrome may also demand extra help or attention in school, although many children are included in regular classes.

Other Resources
The views of these organizations are their own and practise not reflect the official position of CDC.
- Down syndrome Research Foundation (DSRF)external icon
DSRF initiates research studies to better understand the learning styles of those with Down syndrome. - Global Down Syndrome Foundationexternal icon
This foundation is dedicated to significantly improving the lives of people with Down's syndrome through research, medical care, education and advocacy. - National Association for Down's syndromeexternal icon
The National Association for Downward Syndrome supports all persons with Down syndrome in achieving their total potential. They seek to assistance families, educate the public, accost social issues and challenges, and facilitate active participation. - National Down Syndrome Lodge (NDSS)external icon
NDSS seeks to increase awareness and acceptance of those with Down's syndrome.
References
- Mai CT, Isenburg JL, Canfield MA, Meyer RE, Correa A, Alverson CJ, Lupo PJ, Riehle‐Colarusso T, Cho SJ, Aggarwal D, Kirby RS. National population‐based estimates for major birth defects, 2010–2014. Birth Defects Research. 2019; 111(18): 1420-1435.
- Shin 1000, Siffel C, Correa A. Survival of children with mosaic Down syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A:800-1.
- Allen EG, Freeman SB, Druschel C, et al. Maternal age and risk for trisomy 21 assessed by the origin of chromosome nondisjunction: a report from the Atlanta and National Down's syndrome Projects. Hum Genet. 2009 Feb;125(1):41-52.
- Ghosh S, Feingold E, Dey SK. Etiology of Downwardly syndrome: Evidence for consistent association amidst contradistinct meiotic recombination, nondisjunction, and maternal age across populations. Am J Med Genet A. 2009 Jul;149A(7):1415-20.
- Sherman SL, Allen EG, Bean LH, Freeman SB. Epidemiology of Down's syndrome. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2007;xiii(iii):221-7.
- Adams MM, Erickson JD, Layde PM, Oakley GP. Downward'due south syndrome. Recent trends in the United States. JAMA. 1981 Aug 14;246(7):758-threescore.
- Olsen CL, Cross PK, Gensburg LJ, Hughes JP. The effects of prenatal diagnosis, population ageing, and changing fertility rates on the alive nativity prevalence of Downward syndrome in New York Land, 1983-1992. Prenat Diagn. 1996 November;16(11):991-1002.
- Bull MJ, the Committee on Genetics. Wellness supervision for children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics. 2011;128:393-406.
Source: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/downsyndrome.html
0 Response to "Is a Down Syndrome Baby More Likely to Be Breech"
Post a Comment